What is the McKinney-Vento Homeless Assistance Act?
The McKinney-Vento Homeless Assistance Act is a federal law created to support the enrollment and education of homeless students. McKinney-Vento is intended to provide homeless students the same educational opportunities as housed students by removing as many barriers to learning for homeless students as possible.
What are some of the rights are afforded to students and school districts through McKinney-Vento?
- Transportation to and from school and extracurriculars free of charge. This includes ensuring specific busing for homeless students so they can stay at the school they were attending before they became homeless.
- Children experiencing homelessness have the right to attend their school of origin (the school they attended when they first became homeless) even if they are not residing in the area anymore.
- Schools must enroll children immediately even if they lack normally required documents, such as immunization records or proof of residence.
- States must designate a statewide homeless coordinator to review policies and create procedures that affect homeless students.
- Local school districts must appoint Education Liaisons to ensure that school staff are aware of these rights, to provide public notice to homeless families, and to facilitate access to school and transportation services.
How can McKinney-Vento funds be used to assist students?
Examples include, but are not limited to:
- Tutors or other academic supports
- Basic school supplies
- Transportation to and from school and extracurricular activities
- Specialized training and professional development for teachers and other school staffers

How does funding for McKinney-Vento work?
McKinney-Vento funds are distributed to individual states by the U.S. Department of Education in proportion to their Title 1, Part A funding (funding that provides financial assistance to local educational agencies for children from low-income families). The states then distribute these funds to individual school districts through a competitive subgrant process.
More information about the process of applying for McKinney-Vento funds can be found here: http://www.p12.nysed.gov/funding/2019-2022-nysed-mckinney-vento-grant/2019-2022-nysed-mckinney-vento-grant-webinar-slides.pdf
How does McKinney-Vento define homelessness?
The McKinney-Vento Act defines homeless children as “individuals who lack a fixed, regular, and adequate nighttime residence.” This definition includes (but is not limited to) children who are:
- sharing housing due to economic hardship or loss of housing (e.g. doubled-up)
- living in motels, hotels, trailer parks, or campgrounds
- living in emergency or transitional shelters
- sleeping in places unfit for human habitation (e.g. park benches)
- living in cars, parks, public spaces, abandoned buildings, substandard housing, bus or train stations, etc.

This definition was put in place by the U.S. Department of Education and is more inclusive than the definition used by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, which funds the majority of programs that serve homeless families and children.
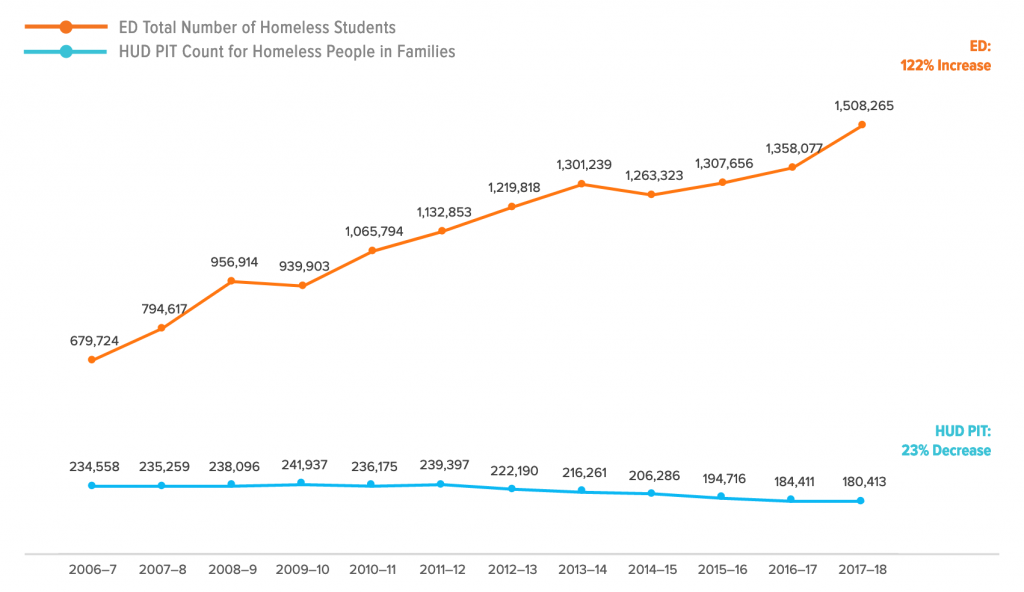
How is the McKinney-Vento count of students that experience homelessness different than the Point-in-Time (PIT) count of families and individuals that are homeless?
The annual Point-in-Time count is a way to measure homelessness that is designed and funded by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). This count provides an estimate of the total number of households and individuals experiencing homelessness as defined by HUD, meaning those who are living in places unfit for human habitation (e.g. on the street) or in shelter. Doubled-up families or those living in paid out-of-pocket hotels/motels are not counted.
The McKinney-Vento count—while not providing an estimate on the number of households that experience homelessness— includes all children that “lack a fixed, regular, and adequate nighttime residence,” including those staying doubled-up and those in paid out-of-pocket hotels and motels.
How does McKinney-Vento identification of homeless students work?
The McKinney-Vento Act requires schools to identify and count students experiencing homelessness as defined by the U.S. Department of Education. Identification of homeless students under McKinney-Vento is a yearlong process. School staff, administrators, and teachers should all be trained in how to identify homeless students. If they believe they know a student who has become homeless, they inform the McKinney-Vento coordinator for their school or district.